MIKROBIOLOGIETEST - FAQ
Was ist ein mikrobiologischer Test?
Ein mikrobiologischer Test ist ein Laborverfahren zur Untersuchung und Charakterisierung von Mikroorganismen wie Bakterien, Hefen, Schimmel und anderen Krankheitserregern. Im Cannabisbereich bezieht sich der Begriff „mikrobiologischer Test“ auf die Zählung der Anzahl von Bakterien, Hefen, Schimmel usw. oder auf die Prüfung, ob ein bestimmter Krankheitserreger im Produkt vorhanden ist oder nicht.
Was ist Log-Reduktion in der Mikrobiologie?
In der Mikrobiologie ist die „log-Reduktion“ ein Maß für die Wirksamkeit eines Prozesses bei der Reduzierung von Krankheitserregern. Je höher die log-Reduktion, desto wirksamer ist der Prozess bei der Abtötung von Krankheitserregern. „Log“ ist die Abkürzung für Logarithmus, ein mathematischer Begriff. Jede log-Erhöhung entspricht einer Verzehnfachung. Zum Beispiel ist 3-log gleich 103 oder 10 x 10 x 10 = 1.000.
Eine Log-Reduktion nimmt die Leistung in die entgegengesetzte Richtung. Beispielsweise entspricht eine Log-Reduktion von 1 einer 10-fachen Reduktion oder die endgültige Zählung ist 1/10 der ursprünglichen Zählung. Die prozentuale Reduzierung ist also (1 - 1/10) x 100 = 90%.
Zur Bestimmung der Log-Reduktion zählen mikrobiologische Labore die Anzahl der koloniebildenden Einheiten (KBE/g) eines bestimmten Mikroorganismus, z. B. TYMC, in einem Produkt vor der Behandlung. Anschließend wird nach der Radiofrequenzbehandlung eine weitere Probe eingesandt, um die KBE/g desselben Erregers zu messen. Die Differenz zwischen „vorher“ und „nachher“ wird als Log-Reduktion ausgedrückt.
Als Faustregel gilt, dass Sie für jede zusätzliche Log-Reduktionszahl eine 9 zur prozentualen Reduktion hinzufügen – also eine Log-Reduktion von 3, wie oben dargestellt, ist (1 - 1/1000) x 100 = 99,91 TP2T-Reduktion im Vergleich zu einer Log Reduktion von 6, was einer Reduktion von 99,99991 TP2T entspricht.
Wofür wird ein Gram-Färbetest in der Mikrobiologie verwendet?
In der Mikrobiologie ist die Gram-Färbung ein Test zur Identifizierung von Bakterien. Eine Probe wird gefärbt und unter dem Mikroskop untersucht, um zu sehen, wie die Bakterien auf die Färbung reagieren. Die Bakterien werden anhand ihrer Farbe als grampositiv oder gramnegativ klassifiziert. Grampositive Bakterien erscheinen violett, während gramnegative Bakterien rosa erscheinen.
Was sind KBE in Cannabis?
CFU steht für Colony Forming Units (koloniebildende Einheiten). Sie gibt die Anzahl der lebenden Mikroorganismen in Cannabis an. Die CFU wird durch Zählen der Kolonien bestimmt, die auf einer Petrischale wachsen.
Welche Mikroben und Krankheitserreger werden bei Cannabistests untersucht?
Die in Cannabisprodukten untersuchten Mikroben und Krankheitserreger variieren und hängen von den staatlichen Vorschriften ab. Zu den häufigsten gehören Gesamthefe und Schimmel (TYMC), Gesamtaerobe Keimzahl (TAMC), Aspergillus, Coliforme, E coliund Galle-Tolerante gramnegative Bakterien (BTGN).
Welche Arten von Tests gibt es auf mikrobielle Kontamination in Cannabis?
Für Cannabispflanzenmaterial werden zwei Arten mikrobieller Tests verwendet. Die erste ist eine kulturbasierte Methode, bei der eine Probe auf selektivem Medium ausgestrichen und unter bestimmten Bedingungen inkubiert wird. um das Wachstum gezielter Mikroben zu ermöglichen. Die gebildeten Kolonien werden dann gezählt, um die mikrobielle Belastung zu bestimmen, ausgedrückt als KBE/g. Die zweite Methode ist die PCR-Methode, die und quantifiziert die spezifische mikrobielle DNA von Krankheitserregern in der Probe.
Hilft die Radiofrequenzbehandlung, mikrobielle Tests zu bestehen?
Die Behandlung mit Radiofrequenz reduziert nachweislich die Gesamtkeimzahl von Hefen und Schimmelpilzen (TYMC) um mehr als 99,91 TP3T und erfüllt die gesetzlichen Anforderungen. Radiofrequenz ist auch bei der Bestimmung anderer Testkriterien wirksam, wie z. B. der Gesamtzahl aerober Mikroorganismen (TAMC), gallentoleranter gramnegativer Bakterien (BTGN), coliformer Bakterien und Aspergillus.
Beseitigt Radiofrequenz Pestizide oder Schwermetalle?
Bei der Radiofrequenzbehandlung steht die Reduzierung mikrobieller Verunreinigungen wie Hefe, Schimmel und Bakterien im Vordergrund, Pestizide oder Schwermetalle werden dabei jedoch nicht behandelt oder eliminiert.
Kann Radiofrequenz Penicillium behandeln?
Penicillium ist eine Schimmelpilzart. Es kommt natürlicherweise in der Umwelt vor (Boden, verrottende Vegetation und Luft).
Wie jeder andere Mikroorganismus umfasst die Familie Penicillium eine breite Palette von Arten, von denen sich einige als sehr nützlich für den Menschen erwiesen haben; zum Beispiel wird das Antibiotikum Penicillin von Penicillium produziert, und der Schimmel, der bei der Herstellung von Camembertkäse verwendet wird, stammt aus der Familie Penicillium
Andererseits gelten viele Penicillium-Arten als Kontaminanten, und einige können beim Menschen sogar Infektionen verursachen oder Mykotoxine produzieren.
Da Radiofrequenz (RF) Hefe- und Schimmelpilzbefall wirksam reduziert, ist davon auszugehen, dass RF auch die Penicillium-Population reduzieren kann. Wir verfügen jedoch nicht über spezifische Daten zu Penicillium-Arten auf Cannabis und können daher keine spezifische Log-Reduktion vorhersagen.
Tötet Radiofrequenz Mykotoxine ab?
Mykotoxine wie Aflatoxine sind natürlich vorkommende Toxine, die von Schimmelpilzen wie Aspergillus produziert werden. Diese Toxine können die Wurzel einer Vielzahl von gesundheitsschädlichen Wirkungen sowohl bei Menschen als auch bei Tieren sein. Immunsuppression (Schwächung des Immunsystems) und Krebs gehören zu den mit Aflatoxinen verbundenen gesundheitlichen Auswirkungen. Die meisten Mykotoxine sind chemisch stabil und werden bei der Lebensmittelverarbeitung nicht vollständig zerstört. Um diese Verbindungen zu eliminieren, sind komplexere und strengere Verarbeitungsbedingungen erforderlich.
In der Vergangenheit haben wir die Wirkung von RF auf die Reduktion von Aflatoxin in Mais getestet und eine gewisse Reduktion der Aflatoxinkonzentrationen bei hohen Temperaturen (110–120°C) beobachtet. Wir haben keine Daten zur Wirkung von RF auf Mykotoxine in Cannabis. Aufgrund früherer Erfahrungen kann man jedoch sagen, dass die HF-Prozesszeit und -temperatur zur Reduzierung der mikrobiellen Population in Cannabis nicht ausreichen, um Mykotoxine zu zerstören.
Können gallentolerante gramnegative Bakterien mit Radiofrequenz behandelt werden?
Gallentolerante gramnegative Bakterien (BTGN) sind eine Bakteriengruppe, die die rauen Bedingungen des menschlichen Magens überleben kann. Sie sind mit einer Membran ausgestattet, die sie vor einer Vielzahl von Chemikalien wie Reinigungsmitteln, antimikrobiellen Enzymen und sogar vielen Antibiotika schützt. Einige Bakterien der Familien Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas und Aeromonas gehören zu den gallentoleranten gramnegativen Bakterien. Sie sind in der Umwelt weit verbreitet.
In den USA verlangen die Aufsichtsbehörden, die die Cannabis-Monographie des American Herbal Pharmacopoeia als Referenz für die Definition des akzeptablen mikrobiellen Grenzwerts in Cannabis verwenden, Tests auf gallentolerante gramnegative Bakterien mit einem akzeptablen Grenzwert von < 1000 KBE/g. Washington, Massachusetts, New Mexico, New York, Illinois und Ohio gehören zu den Staaten, in denen Tests auf gallentolerante gramnegative Bakterien erforderlich sind.
Kanadische Vorschriften verlangen Tests auf gallentolerante gramnegative Bakterien in Cannabis. Ziel hat begrenzte Erfahrung mit der Sanierung von BTGN, jedoch verfügt Ziel zu diesem Zeitpunkt nicht über ausreichende Daten, um die erwartete Protokollreduzierung von BTGN mit dem Baseline-Rezept vorherzusagen.
Kann Radiofrequenz tödlich sein? Aspergillus?
In begrenzten Produktionsläufen mit Cannabisblüten, die positiv getestet wurden auf Aspergillus, Radio Frequency konnte dieses Produkt erfolgreich konform machen.
Wächst Schimmel oder Hefe nach einer Radiofrequenzbehandlung nach?
Nein. Solange der Wasseraktivitätswert unter 0,65 liegt, können Schimmel, Hefen und Bakterien nicht nachwachsen. Analysezertifikate geben in der Regel den Wasseraktivitätswert an. Darüber hinaus verlangen einige Bundesstaaten einen Wasseraktivitätswert < 0,65 oder 0,60, um die Produktstabilität nach der Abgabe in den Apotheken zu gewährleisten.
Sollten Züchter häufig vorkommende Schimmelpilze identifizieren, bevor sie eine Radiofrequenzbehandlung durchführen?
Die Züchter müssen vor der Behandlung nicht die Art des Schimmels bestimmen.
Kann Radiofrequenz Mehltau beseitigen?
Leider nein. Mit fortschreitendem Schimmelbefall kommt es zu optischen Beeinträchtigungen. Es gibt kein Sanierungsverfahren, das den Echten Mehltau entfernen kann. Wir empfehlen, die Prozesse vor der Ernte zu verbessern, den Nachernteprozess effektiv zu managen und die Behandlung mit Radiofrequenz durchzuführen.
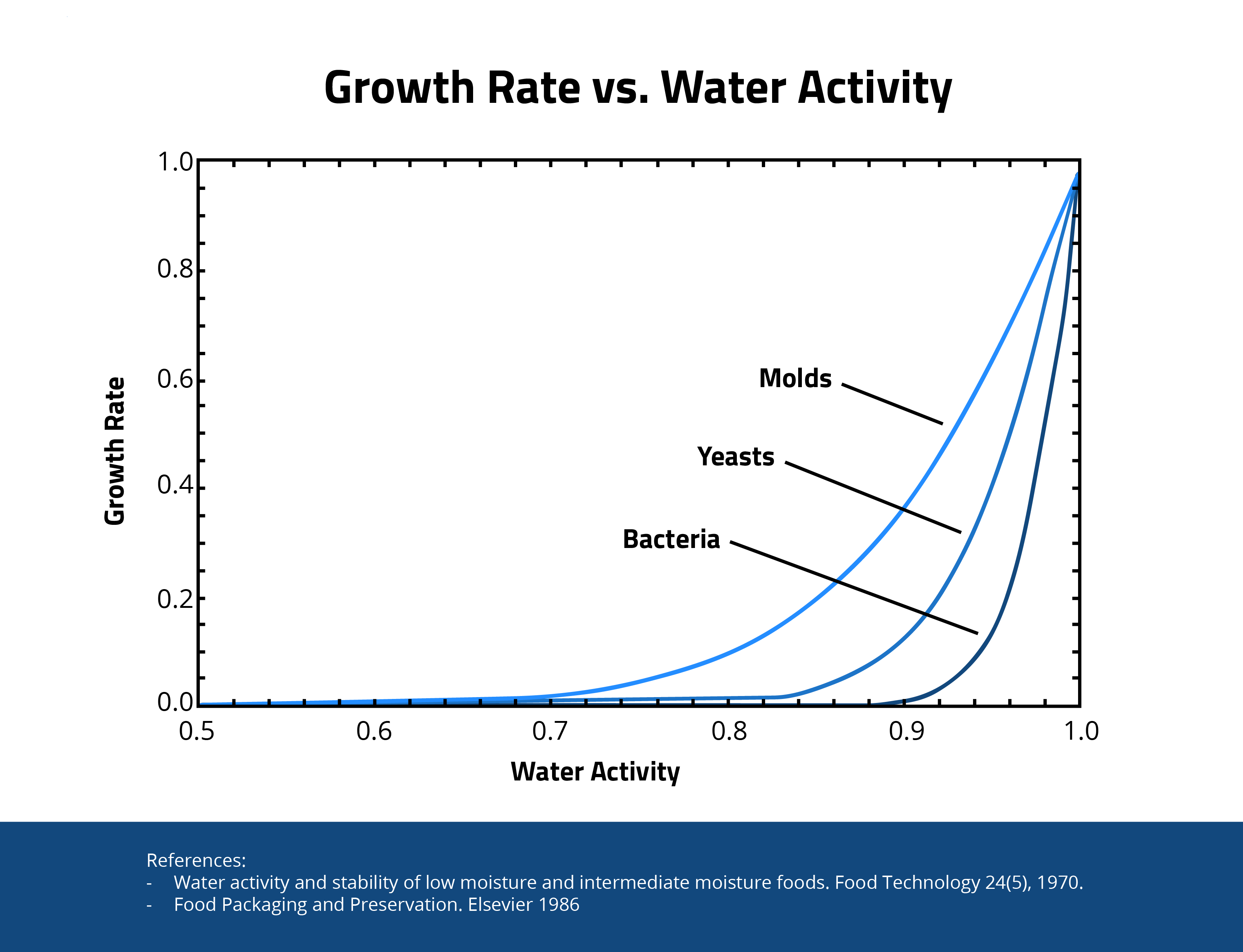
Tritt eine Regeneration ein, nachdem das Produkt mit Hochfrequenz behandelt wurde?
Nein. Wie aus der Tabelle hervorgeht, wachsen Schimmelpilze, Hefen und Bakterien nicht nach, solange die Wasseraktivität unter 0,65 liegt. Analysenzertifikate messen in der Regel die Wasseraktivität. Darüber hinaus verlangen einige Staaten Wasseraktivitätswerte < 0,65 oder 0,60, um die Produktstabilität zu gewährleisten, nachdem es in Einzelhandelsapotheken platziert wurde.
Weitere Ressourcen zum Thema ionisierende und nichtionisierende Strahlung


Ziel erhält das allererste Patent zur mikrobiellen Behandlung von Cannabis