MICROBIOLOGY TEST - FAQ
What is a microbiology test?
A microbiology test is a laboratory procedure to examine and characterize microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast, mold and other pathogens. In cannabis the term “microbiology testing” refers to counting the number of bacteria, yeast, mold, etc., or testing whether a specific pathogen is present in the product or not.
What is log reduction in microbiology?
In microbiology “log reduction” is a measure of how effective a process is at reducing pathogens. The greater the log reduction the more effective the process is at killing pathogens. ‘Log’ is short for logarithm, a mathematical term. Every ‘log’ increase is a 10-fold increase. For example, 3-log is 103 lub 10 x 10 x 10 = 1000.
Redukcja logu powoduje przeniesienie mocy w przeciwnym kierunku. Na przykład redukcja log o 1 jest równoważna 10-krotnej redukcji lub ostateczna liczba wynosi 1/10 pierwotnej liczby. Zatem procentowa redukcja wynosi (1 - 1/10) x 100 = 90%.
To determine the log reduction, microbiology labs count the number of colony-forming units (CFU/g) of a given microorganism, e.g., TYMC, in a product before treatment. Then another sample is sent after Radio Frequency treatment to measure CFU/g of the same pathogen. The result of the difference between the ‘before’ and the ‘after’ is expressed as a Log Reduction.
Ogólna zasada jest taka, że do każdej dodatkowej wartości redukcji logu dodaje się 9 do procentowej redukcji – zatem redukcja log o 3, jak pokazano powyżej, to (1 – 1/1000) x 100 = redukcja 99,9% w porównaniu z logarytmem redukcja o 6, co jest równoważne redukcji o 99,9999%.
What is a gram stain test used for in microbiology?
In microbiology, a gram stain is a test used to identify bacteria. A sample is stained and examined under a microscope to see how the bacteria react to the stain. The bacteria are classified as either Gram-positive or Gram-negative based on the color they turn. Gram-positive bacteria appear purple, while Gram-negative bacteria appear pink.
What are CFUs in cannabis?
CFU stands for Colony Forming Units. It indicates the number of living microorganisms in cannabis. CFU is determined by counting the number of colonies that grow on a Petri dish.
What microbes and pathogens are screened in cannabis testing?
The microbes and pathogens screened in cannabis products vary and depend on state regulations. Some of the common ones include Total Yeast and Mold (TYMC), Total Aerobic Count (TAMC), Aspergillus, Coliforms, E coli, and Bile-Tolerant Gram-negative Bacteria (BTGN).
What are the types of tests for microbial contamination in cannabis?
Two types of microbial testing are used for cannabis plant material. The first is a culture-based method involving plating a sample on selective media and incubating it under specific conditions to allow the growth of targeted microbes. The colonies formed are then counted to determine the microbial load, expressed as CFU/g. The second is the PCR method, which detects and quantifies specific microbial DNA of pathogens in the sample.
Will Radio Frequency treatment help pass microbial testing?
Treatment with Radio Frequency is proven to reduce Total Yeast and Mold Count (TYMC) by more than 99.9% and comply with regulatory requirements. Radio Frequency is also effective in addressing other testing criteria such as Total Aerobic Microbial Count (TAMC), Bile-Tolerant Gram-Negative (BTGN), Coliforms, and Aspergillus.
Does Radio Frequency eliminate pesticides or heavy metals?
Radio Frequency treatment focuses on reducing microbial contamination, such as yeast, mold, and bacteria, but it does not address or eliminate pesticides or heavy metals.
Can Radio Frequency Treat Penicillium?
Penicillium to rodzaj pleśni. Występuje naturalnie w środowisku (glebie, rozkładającej się roślinności i powietrzu).
Like any other microorganism, Penicillium family includes a wide range of species from which a few have been proven to be very beneficial to humans; for example, antibiotic penicillin is produced by Penicillium, and the mold used in making Camembert cheese is from the Penicillium family
Z drugiej strony wiele gatunków Penicillium uważa się za substancje zanieczyszczające, a niektóre mogą nawet powodować infekcje u ludzi lub wytwarzać mikotoksyny.
Knowing that Radio Frequency (RF) is effective in total yeast and mold reduction, it is expected that RF can reduce Penicillium population. However, we do not have data specifically related to Penicillium species on cannabis and cannot predict specific log reduction.
Does Radio Frequency kill mycotoxins?
Mikotoksyny, takie jak aflatoksyny, to naturalnie występujące toksyny wytwarzane przez pleśnie, takie jak Aspergillus. Toksyny te mogą być przyczyną różnych niekorzystnych skutków zdrowotnych zarówno u ludzi, jak i zwierząt. Do skutków zdrowotnych związanych z aflatoksynami zalicza się supresja odporności (osłabienie układu odpornościowego) i nowotwory. Większość mikotoksyn jest stabilna chemicznie i nie ulega całkowitemu zniszczeniu podczas przetwarzania żywności. Aby wyeliminować te związki, wymagane są bardziej złożone i surowe warunki przetwarzania.
W przeszłości testowaliśmy wpływ RF na redukcję aflatoksyn w kukurydzy i zaobserwowaliśmy pewne zmniejszenie stężenia aflatoksyn w wysokich temperaturach (110-120°C). Nie mamy żadnych danych na temat wpływu RF na mikotoksyny w konopiach indyjskich. Jednakże na podstawie wcześniejszych doświadczeń można stwierdzić, że czas i temperatura procesu RF w celu redukcji populacji drobnoustrojów w konopiach indyjskich nie są wystarczające do zniszczenia mikotoksyn.
Can Radio Frequency treat bile-tolerant gram-negative bacteria?
Bile-tolerant gram-negative (BTGN) bacteria are a group of bacteria that could survive the harsh condition of the human stomach. They are equipped with a membrane that protects them against a wide range of chemicals such as detergents and antimicrobial enzymes or even many antibiotics. Some bacteria from Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomona and Aeromonas families are members of the bile-tolerant gram-negative bacteria. They are widely spread in the environment.
W USA agencje regulacyjne, które wykorzystują monografię Cannabis Monograph American Herbal Pharmacopoeia jako punkt odniesienia przy określaniu dopuszczalnego limitu mikrobiologicznego w konopiach indyjskich, wymagają przeprowadzenia badań na obecność bakterii Gram-ujemnych tolerujących żółć z akceptowalnym limitem < 1000 CFU/g. Waszyngton, Massachusetts, Nowy Meksyk, Nowy Jork, Illinois i Ohio należą do stanów, w których wymagane są badania na obecność bakterii Gram-ujemnych tolerujących żółć.
Kanadyjskie przepisy wymagają badania konopi indyjskich na obecność bakterii Gram-ujemnych tolerujących żółć. Ziel ma ograniczone doświadczenie w naprawie BTGN, jednak w tym momencie Ziel nie ma odpowiednich danych, aby przewidzieć oczekiwaną redukcję logarytmiczną BTGN przy zastosowaniu receptury bazowej.
Can Radio Frequency kill Aspergillus?
In limited production runs on cannabis flower that tested positive for Aspergillus, Radio Frequency was able to successfully bring that product to compliance.
Does mold or yeast regrow after Radio Frequency treatment?
No. As long as the water activity level is below 0.65, molds, yeasts, and bacteria will not grow back. Certificates of Analysis usually measure water activity levels. In addition, some states require water activity levels < 0.65 or 0.60 to ensure product stability after it is placed in retail dispensaries.
Should cultivators identify common molds before Radio Frequency treatment?
Cultivators don't need to identify the type of mold before treatment.
Can Radio Frequency fix powdery mildew?
Unfortunately, no. As the mold advances, visual impairment occurs. There is no remediation process that can remove the powdery mildew. The recommendations are to improve your upstream processes prior to harvest, manage the post-harvesting process effectively, and remediate with Radio Frequency.
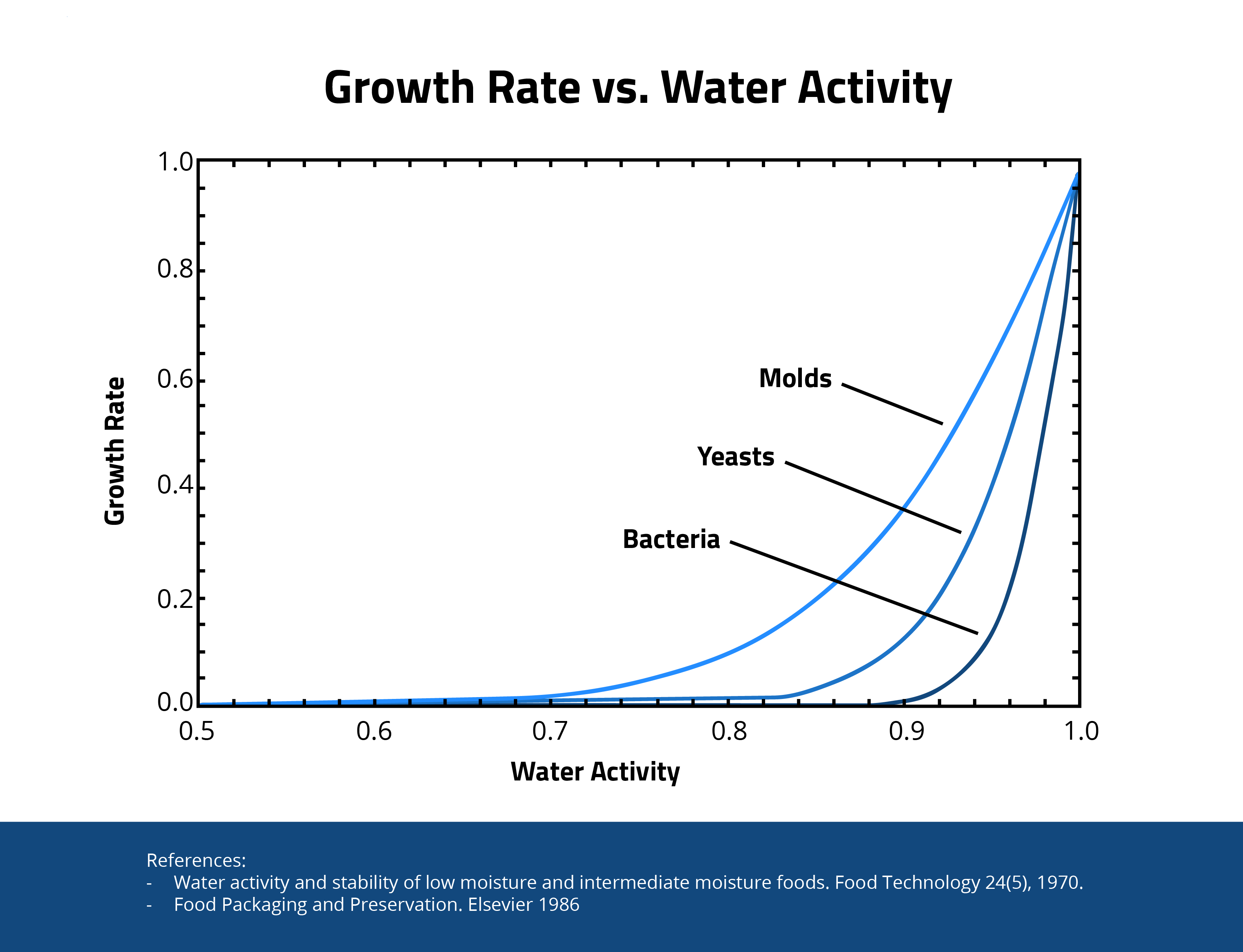
Czy regeneracja następuje po poddaniu produktu działaniu częstotliwości radiowej?
Nie. Jak wynika z wykresu, dopóki poziom aktywności wody jest niższy niż 0,65, pleśnie, drożdże i bakterie nie będą odrastać. Certyfikaty analizy zwykle mierzą poziom aktywności wody. Ponadto w niektórych stanach wymagane są poziomy aktywności wody < 0,65 lub 0,60, aby zapewnić stabilność produktu po umieszczeniu go w punktach sprzedaży detalicznej.
Więcej zasobów na temat promieniowania jonizującego i niejonizującego


Ziel otrzymał pierwszy w historii patent na leczenie mikrobiologiczne konopi indyjskich

Ziel otrzymuje zatwierdzenie GMP UE w zakresie kontroli mikrobiologicznej
